Adaptive optics pinpoints 2 supermassive black holes in colliding galaxies
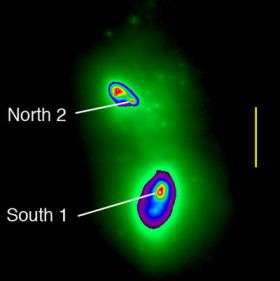
Astronomers have discovered the exact location and makeup of a pair of supermassive black holes at the center of a collision of two galaxies more than 300 million light years away.
Using adaptive optics (AO), which clear the blurring effects of turbulence in the Earth's atmosphere, Livermore scientists observed that the two black holes formed at the center of a rotating disk of stars in the galaxy merger known as NGC 6240 and are surrounded by a cloud of young star clusters.
Supermassive black holes contain millions to billions of times the mass of the sun and are believed to exist in the center of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way.
For years, astronomers have known that NGC 6240 hosted at least one supermassive black hole. Later observations at NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory confirmed that there were actually two supermassive black holes in the core of NGC 6240. And the new research, which appears in the May 17 edition of Science Express, confirms the exact location and environment of the two black holes from observations at the W.M. Keck Observatory.
"People had observed this pair of colliding galaxies at different wavelengths and seen what they thought were the black holes, but it's been very hard to make sense of how the observations at various wavelengths correspond to each other," said Claire Max, lead author of the paper. Max is an astronomer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's Institute for Geophysics and Planetary Physics and a faculty member at UC Santa Cruz. "The adaptive optics results enabled us to tie it all together, so now we can really see it all – the hot dust in the infrared, the stars in the visible and infrared, and the X-rays and radio emissions coming from right around the black holes."
Adaptive optics enables astronomers to minimize the blurring effects of the Earth's atmosphere, producing images with unprecedented detail and resolution. The adaptive optics system uses light from a relatively bright star, or guide star, to measure the atmospheric distortions and to correct for them, but only about 1 percent of the sky contains stars sufficiently bright to be of use. A laser built by LLNL has been commissioned at Keck, in which adaptive optics can be used nearly anywhere in the sky by producing an artificial laser guide star.
Other Livermore researchers include Willem de Vries of IGPP and UC Davis and former LLNL postdoctoral researcher Gabriela Canalizo, who is now a faculty member at UC Riverside.
The spatial resolution using adaptive optics at the 10-meter Keck II telescope is an improvement of a factor of 10 over what can be done with conventional ground-based imaging.
Hubble Space Telescope images show that the two black holes are surrounded by patchy dust that partially obscures visible light. However, in the infrared light used in the Keck AO observations, the black holes are more distinct and are surrounded by many young star clusters that formed in the merger.
"With the infrared images we got at Keck, we were able to line up the information from all the different wavelengths to determine which features in the images are the black holes," said Max, who also serves as director at the Center for Adaptive Optics at UC Santa Cruz.
Galaxy mergers are thought to play a major role in galaxy evolution and may help explain many of their properties. For example, astronomers have found that the mass of the black hole at the center of a galaxy is highly correlated with large-scale properties of the galaxy itself. The "coevolution" hypothesis explains this correlation as the result of both the black hole and the galaxy around it growing incrementally in repeated merger events over cosmic time scales.
"The gravitational influence of the black hole is actually limited to a relatively small region right around it, so how can it affect the rest of the galaxy" But if the black hole and the galaxy around it evolved together through the same sequence of merger events, that would explain the correlations," Max said. "That's why people are so excited about understanding galaxy mergers, and here we're seeing it in action."
Source: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory




















